Why is there a limit to the operating temperature of cooling fans? (Part 1)
 Feng Zhi Yuan
Feng Zhi Yuan
 Sep 12,2025
Sep 12,2025
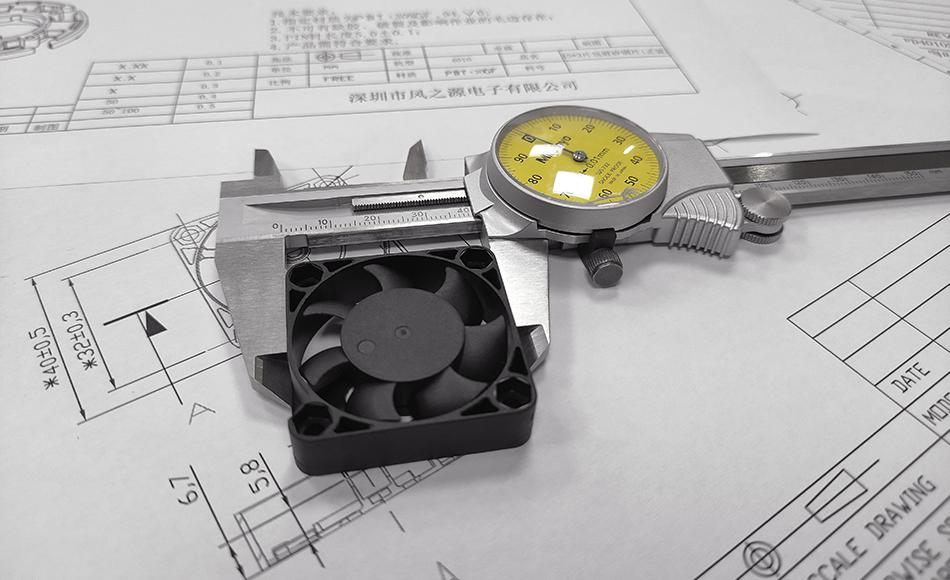
Cooling fans are indispensable components in electronic devices, as they dissipate heat by moving air, ensuring the normal operation of the equipment. However, the operating temperature of cooling fans is not unlimited; they have minimum and maximum limits. Below are some reasons for these limits and their impact on device performance.
1. Thermal sensitivity of motor
The core of a cooling fan lies in its motor, whose coils and magnets are highly sensitive to temperature. At low temperatures, the lubricant of the motor may become viscous, increasing the resistance during startup, thus making it difficult for the motor to start or causing overload. Conversely, at high temperatures, the insulating material of the motor may deteriorate, elevating the risk of short circuits. For instance, at -10°C, the viscosity of the lubricant increases by 30%, leading to an increase in starting current.
2. Thermal expansion and contraction of materials
The blades and frames of fans are typically made of plastic, metal, or other synthetic materials. These materials expand or contract when exposed to temperature changes. Extreme low temperatures may make the materials brittle and prone to cracking, while extreme high temperatures may cause the materials to deform, affecting the balance and efficiency of the fan. For example, the hardness of aluminum alloy increases by about 15% at -40°C compared to 20°C, and it may deform at 100°C.






 Home
Home
 Why is there a limit to the operating temperature of cooling fans? Part 2
Why is there a limit to the operating temperature of cooling fans? Part 2